Understanding McClelland’s Theory of Needs: A Practical Guide for Managers
Understanding McGregor's Theory X and Theory Y: A Comprehensive Exploration
In the mid-20th century, management thinking underwent a revolution that fundamentally changed how organizations approached leadership and employee motivation. At the forefront of this transformation was Douglas McGregor, an American social psychologist, whose work introduced two contrasting theories of human behavior at work: Theory X and Theory Y. These theories not only shaped management practices but also provided a lens through which we can understand the dynamics between managers and employees.
The Birth of Theory X and Theory Y
Douglas McGregor introduced Theory X and Theory Y in his seminal book, "The Human Side of Enterprise," published in 1960. His theories were a response to the prevailing management styles of the time, which were heavily influenced by the industrial revolution and the work of earlier theorists like Frederick Taylor and Henry Fayol. McGregor argued that traditional management practices often stemmed from certain assumptions about human nature, which he encapsulated in Theory X. In contrast, he proposed Theory Y as a more progressive and humanistic alternative.
Historical Context and Development
McGregor's ideas were shaped by his background in psychology and his observation of workplace dynamics during the post-World War II era. This period saw a significant shift from rigid industrial structures to more flexible, knowledge-based work environments. McGregor's insights into human motivation and behavior were heavily influenced by the works of Abraham Maslow, whose hierarchy of needs provided a foundation for understanding employee motivation. By challenging the authoritarian management styles prevalent in his time, McGregor laid the groundwork for modern human-centered management practices.
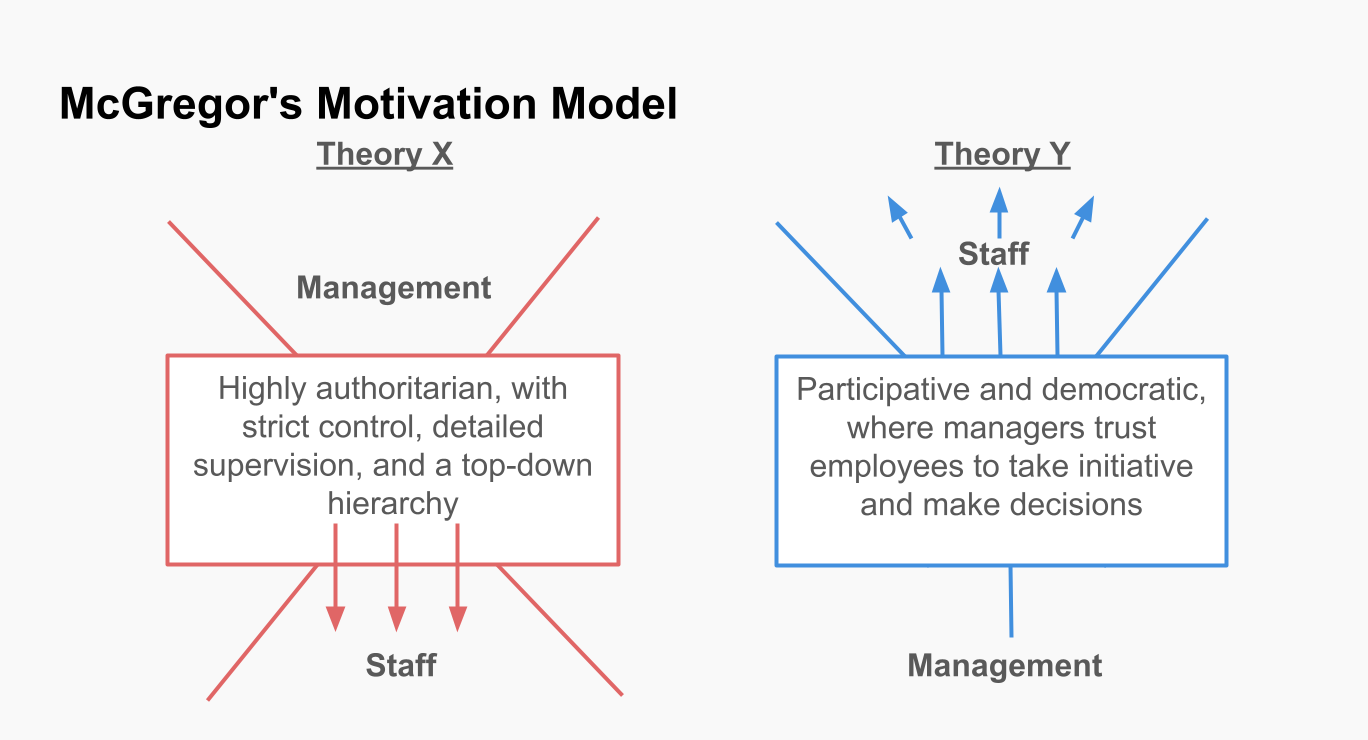
Theory X: The Authoritarian Approach
Theory X represents a pessimistic view of human nature. According to this theory, managers believe that employees inherently dislike work and must be coerced, controlled, or threatened with punishment to achieve organizational goals. The assumptions underlying Theory X include:
- Inherent Dislike for Work. Employees are assumed to be naturally lazy and will avoid work whenever possible.
- Lack of Ambition. Employees prefer to be directed rather than taking responsibility or initiative.
- Need for Control. Managers believe they must closely supervise employees and enforce strict rules to ensure productivity.
- Motivation through Fear. The primary motivators in Theory X are threats and punishments, as employees are thought to be driven mainly by financial incentives and the fear of losing their jobs.
Managers who adhere to Theory X typically adopt an authoritarian style, characterized by tight control, a rigid hierarchy, and a lack of trust in their employees. This approach can lead to a high level of oversight and a work environment where creativity, innovation, and employee engagement are stifled.
Theory Y: The Participative Approach
In contrast, Theory Y offers an optimistic view of human nature. McGregor proposed that managers who embrace Theory Y believe that employees are capable of self-direction, enjoy their work, and are motivated by more than just financial rewards. The key assumptions of Theory Y include:
- Work as a Natural Activity. Employees view work as a natural part of life and can find it as fulfilling as play or rest.
- Self-Motivation. Given the right conditions, employees are self-motivated and do not require constant supervision.
- Capacity for Creativity. Employees are creative and can contribute innovative ideas to solve problems.
- Seeking Responsibility. Employees seek responsibility and can achieve personal and professional goals when empowered to do so.
- Intrinsic Motivation. Employees are motivated by factors such as achievement, recognition, responsibility, and personal growth.
Managers who adopt Theory Y are more likely to foster a participative management style, characterized by trust, collaboration, and a focus on employee development. This approach encourages a work environment where employees are empowered to contribute their best, leading to higher levels of job satisfaction and organizational performance.
Comparing Theory X and Theory Y
The distinction between Theory X and Theory Y is not just about different management styles; it reflects fundamentally different views of human nature and the role of management. Let’s explore their key differences:
- Management Style. Theory X leads to a top-down, authoritarian style of management, whereas Theory Y supports a more democratic, participative approach.
- Motivation. Theory X relies on external motivators, such as financial rewards and punishment, while Theory Y emphasizes intrinsic motivators, like personal growth and job satisfaction.
- Employee Potential. Theory X views employees as limited in their potential, while Theory Y sees them as capable of growth and development.
- Organizational Culture. Theory X creates a culture of control and compliance, whereas Theory Y fosters a culture of trust and innovation.
Introducing Theory Z
Beyond Theory X and Theory Y, another significant contribution to management thinking is Theory Z, developed by Dr. William Ouchi. Theory Z blends American and Japanese management philosophies, emphasizing long-term job security, consensual decision-making, and individual responsibility within a group context. Key elements of Theory Z include:
- Focus on Employee Well-being. Prioritizing the holistic development and satisfaction of employees.
- Collective Decision-making. Encouraging participation and consensus in organizational decisions.
- Job Security. Providing long-term employment to build loyalty and reduce turnover.
Theory Z offers an alternative perspective on management, highlighting the importance of trust and teamwork in achieving organizational success.
Application in Modern Workplaces
In today's dynamic workplaces, the principles of Theory Y and Theory Z are increasingly relevant. Organizations are shifting towards remote work, flexible schedules, and flat hierarchies. For example, companies like Google and Zappos exemplify Theory Y by fostering open communication, employee autonomy, and personal development. Similarly, Theory Z principles can be seen in collaborative team environments and cultures that prioritize employee satisfaction and retention.
However, Theory X still has its place in certain scenarios. For example, in industries requiring strict compliance or during crises, a more authoritative approach may be necessary to maintain control and ensure safety.
Criticisms and Limitations
Despite their influence, McGregor's theories are not without criticism. Some argue that the dichotomy between Theory X and Theory Y is overly simplistic and does not account for the complexity of human behavior. Employees may not fit neatly into either category; their motivation and behavior can vary depending on the context, personal circumstances, and the organizational environment.
Moreover, the rigid categorization can lead to stereotyping, where managers might label employees as "Theory X" or "Theory Y" types, potentially overlooking the need for a more nuanced and flexible approach to management.
Another criticism is that McGregor's theories do not sufficiently address the impact of organizational structures, cultural differences, or economic conditions on management practices. For example, in some industries or cultures, a more authoritative approach might be necessary due to safety concerns or traditional hierarchical norms.
Quiz: Identify whether your management style aligns more with Theory X, Theory Y, or Theory Z.
1. Do you believe employees are naturally inclined to avoid work?
- Yes: Theory X
- No: Theory Y or Z
2. Do you trust employees to take initiative without supervision?
- Yes: Theory Y or Z
- No: Theory X
3. How important is job security in your management style?
- Very Important: Theory Z
- Moderately Important: Theory Y
- Not Important: Theory X
4. Do you prioritize employee collaboration in decision-making?
- Yes: Theory Y or Z
- No: Theory X
5. Which motivates employees more: financial incentives or personal growth?
- Financial Incentives: Theory X
- Personal Growth: Theory Y or Z
Results Interpretation:
Mostly Theory X answers: Your style leans toward an authoritative approach.
Mostly Theory Y answers: You align with a participative management style.
Mostly Theory Z answers: You emphasize long-term collaboration and well-being.
Conclusion
Douglas McGregor's Theory X and Theory Y remain a foundational concept in the field of management, offering valuable insights into human behavior and the dynamics between managers and employees. While the binary nature of these theories may not capture the full complexity of organizational life, they serve as a powerful tool for reflecting on and improving management practices. As organizations continue to evolve in an increasingly complex and fast-paced world, the lessons from Theory X and Theory Y remain relevant, guiding leaders to create environments where employees can thrive and contribute to their fullest potential.
About the Author
Violetta Chernobuk is a skilled content strategist and writer at Planyway, specializing in crafting insightful and engaging articles on productivity and project management. With her keen eye for detail and a deep understanding of user needs, Violetta ensures that every piece of content is both informative and inspiring, helping readers optimize their workflows and stay ahead in their projects.


